Test Method
-
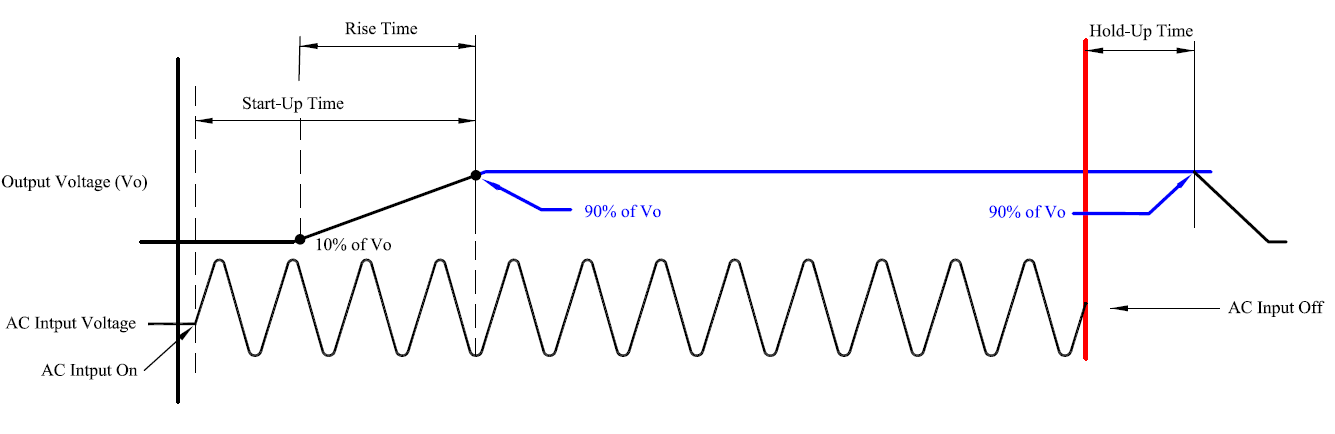
Start-up Time, Rise Time, and Hold-up Time
1.Start-up Time:
The time required for the output voltage to reach 90% of its set value after the input voltage is applied.
2.Rise Time:
The time required for the output voltage to reach from 10% to 90% of its set value.
3.Hold-up Time:
The time as the AC input was declined but the output voltage remains regulation for a period of time.
-
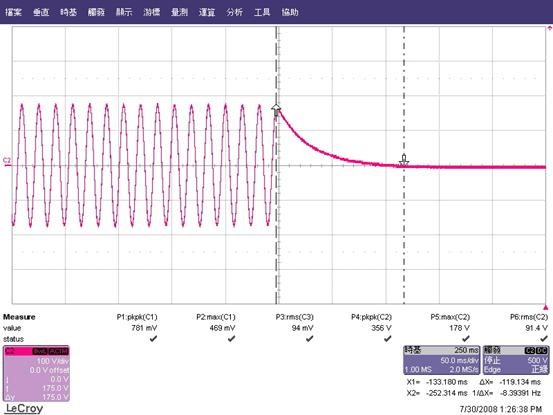
AC discharge test
Measurement of voltage of stored charge 1 second after disconnection of mains plug.
-
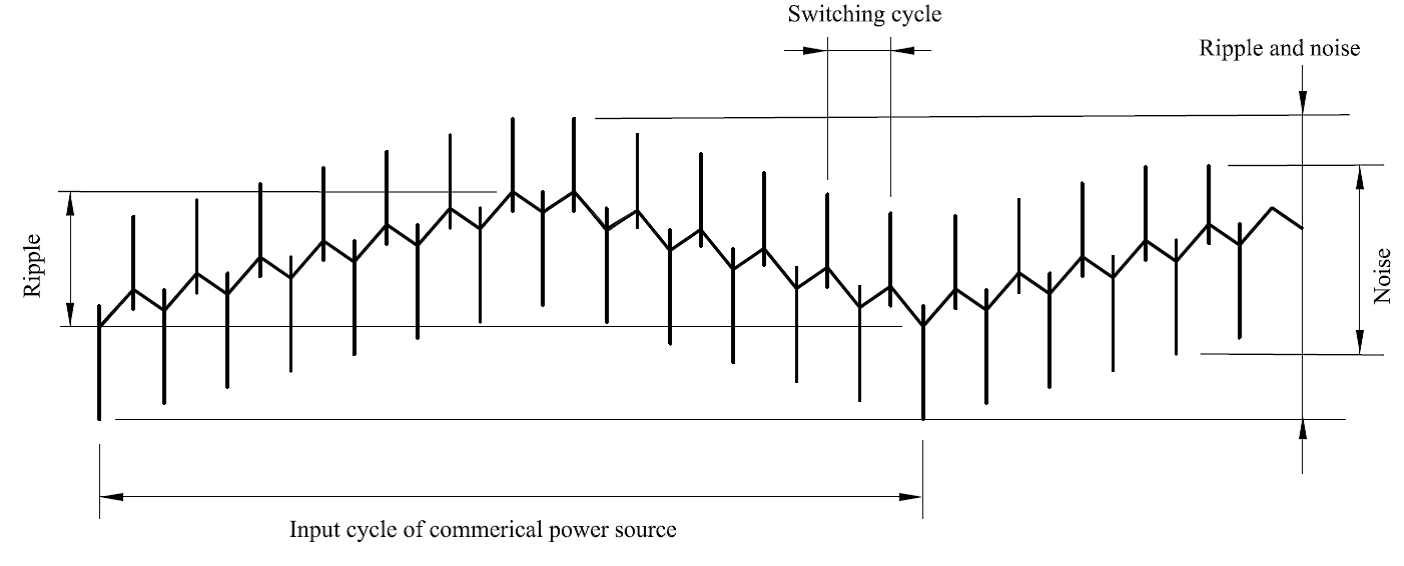
Ripple & Noise
The amplitude of the AC component of the DC output of a power supply usually showed in millivolts peak-to-peak or rms. For a liner power supply it is usually at the frequency of the AC mains. For a switching power supply, it is normally at the switching frequency of the converter stage.
-
Classification of Applied Parts
Type B
 – No electrical contact with Patient and maybe earthed
– No electrical contact with Patient and maybe earthedType BF
 – Electrically connected to Patient but not directly to heart
– Electrically connected to Patient but not directly to heartType CF
 – Electrically connected to the heart of the Patient.
– Electrically connected to the heart of the Patient.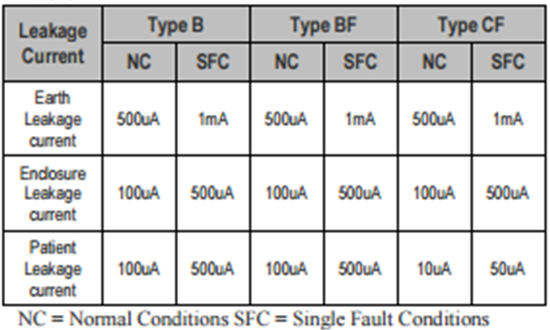
-
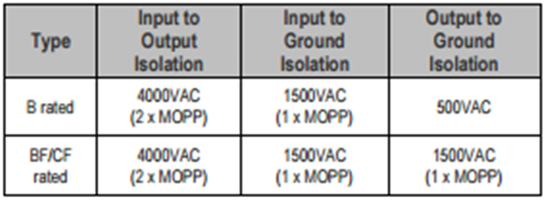
MOOP & MOPP
Means of Patient Protection (MOPP) and Means of Operator Protection (MOOP). It is the responsibility of the medical product manufacturer to determine the likelihood of a patient coming into contact, and decide whether patient protection (MOPP) or operator protection (MOOP) to use.
-
Ground Continuity Test
Determining effectiveness of “ground” grids and connections that are used with the power device to protect personnel and equipment.
-
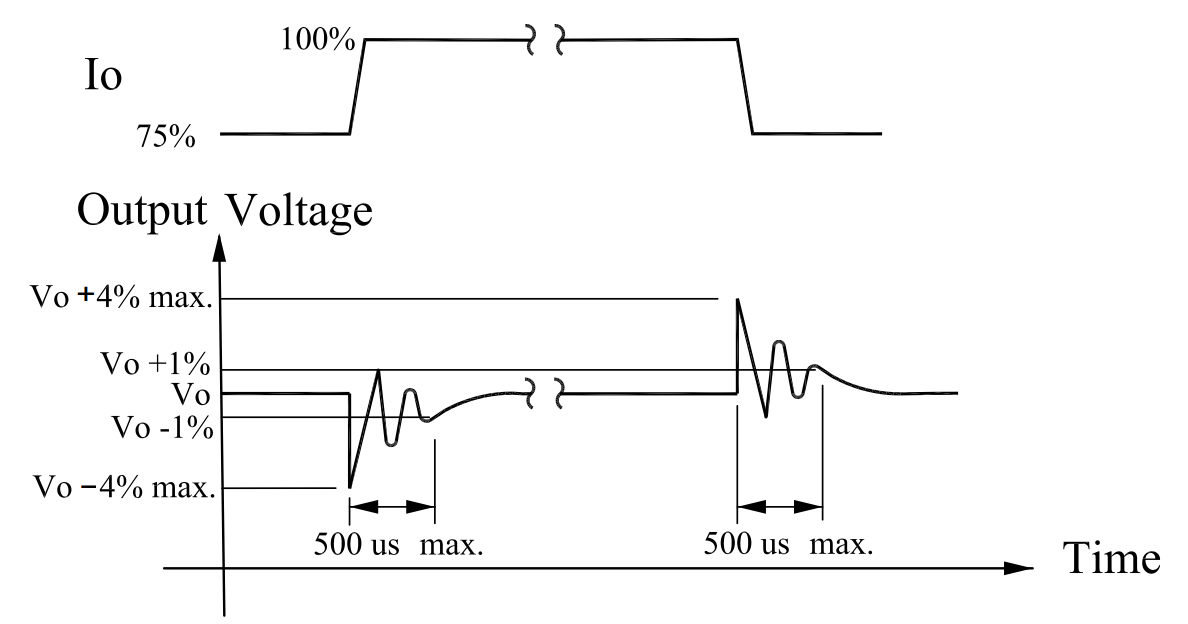
Transient Response
The time needed for an output voltage to be within specified exactness limits after a step change in line or load situations.