常見問題
-
Remote Sense
A method of compensating the decline of regulation caused by the voltage drop in output cables or the device.
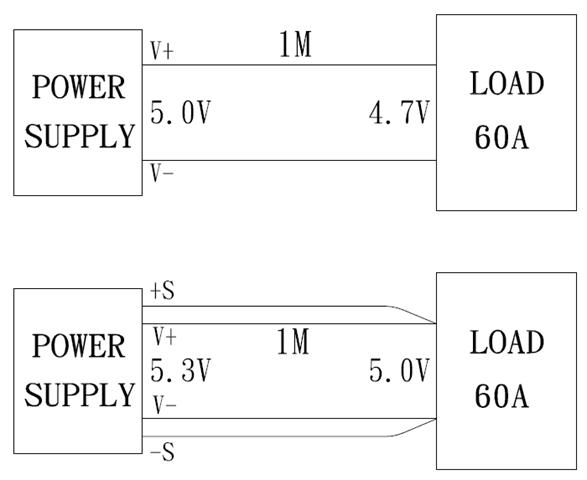
-
N+1 Redundancy & Hot Swap
Redundant operation is used in parallel connections of N Power Supplies (single operation when N = 1) of the same model, where a redundant Power Supply is added to the number of Power Supplies (N) in parallel operation (N+1), thereby improving the reliability of the system.
Hot Swap is replacing or adding components without stopping or shutting down the system.
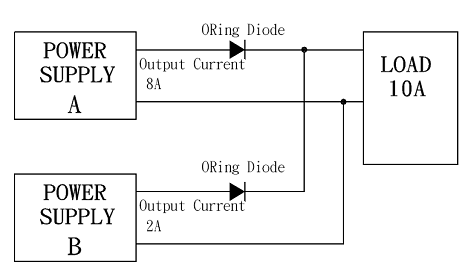
-
Current share
Current sharing is the technique in which power supplies are connected in parallel to provide more load current or redundant power to a load. This connection increases the amount of current available for the load while the voltage remains constant.
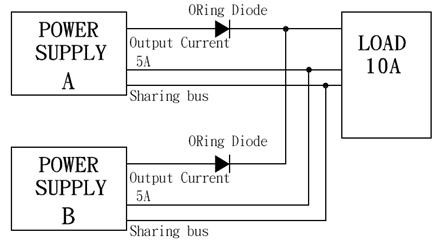
-
Standby Power
Standby Power refers to the electric power consumed by electronic and electrical appliances while they are switched off or in a standby mode.
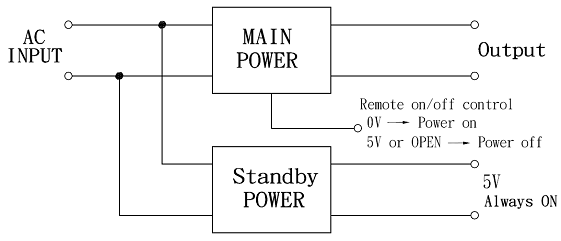
-
PFD Signal (Power Fail Detector)
A feature in a microprocessor supervisory circuit that provides early warning to the microprocessor of imminent power failure.
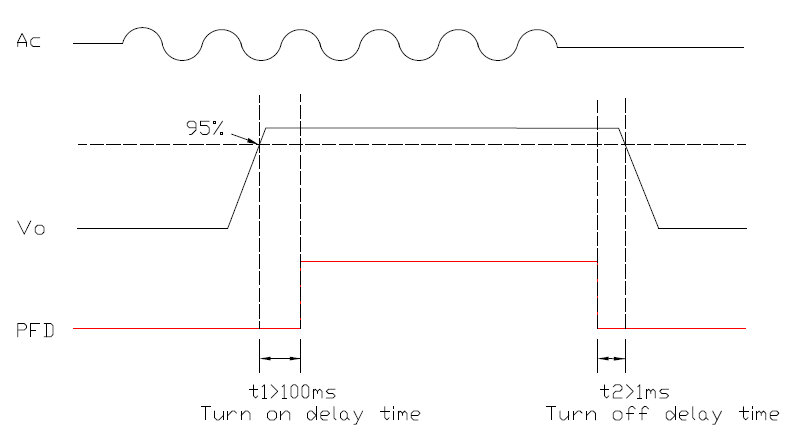
-
Inhibit (Remote on/off)
The inhibit or enable function allows the user to electronically turn on or off the output voltage of a power supply without having to interrupt the input AC or DC voltage with a relay or switch. This is useful during initial set up of the system, during maintenance or for saving energy during periods of non-operation.
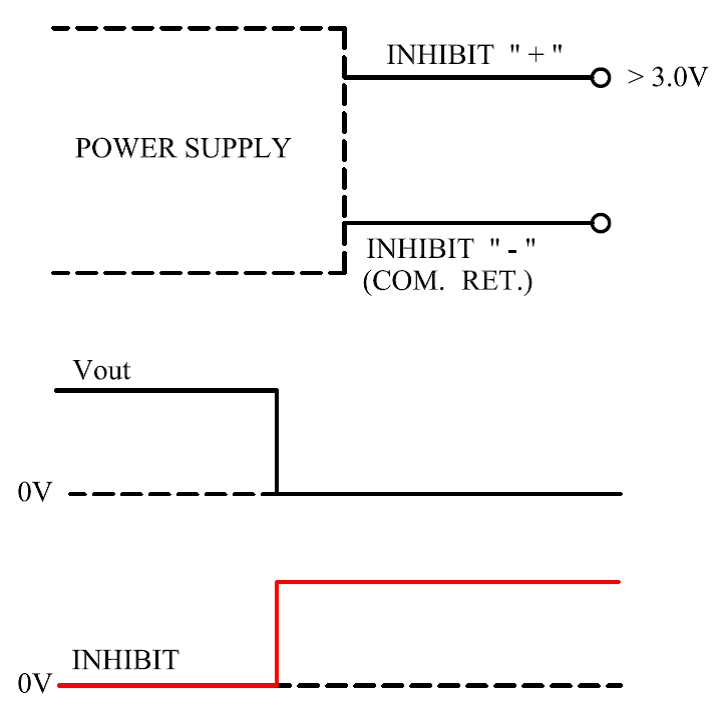
-
DC OK
The DC-OK signal (also called ''power good signal'') monitors the output voltage that is generated from the power supply and is independent of whether an external voltage is fed into the system or not.
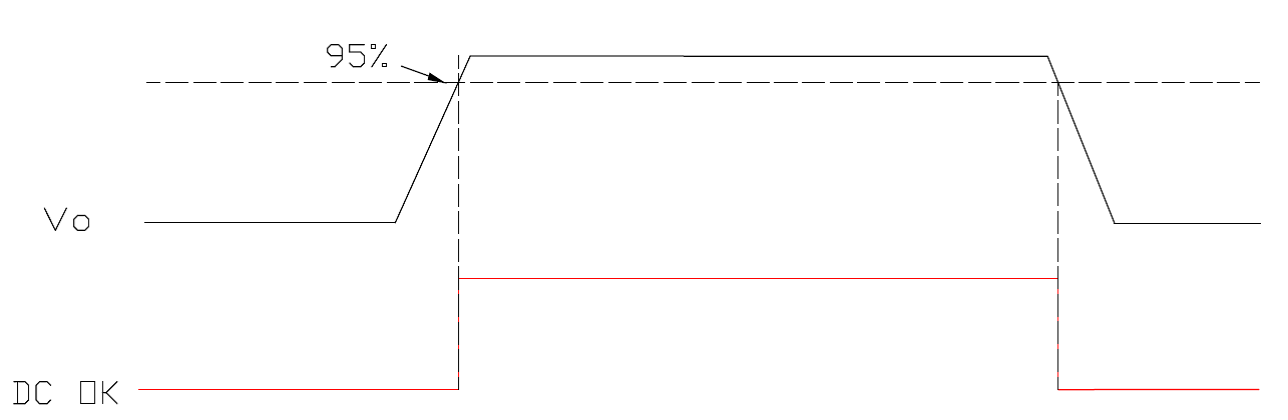
-
Peak Current Duty Cycle Calculation
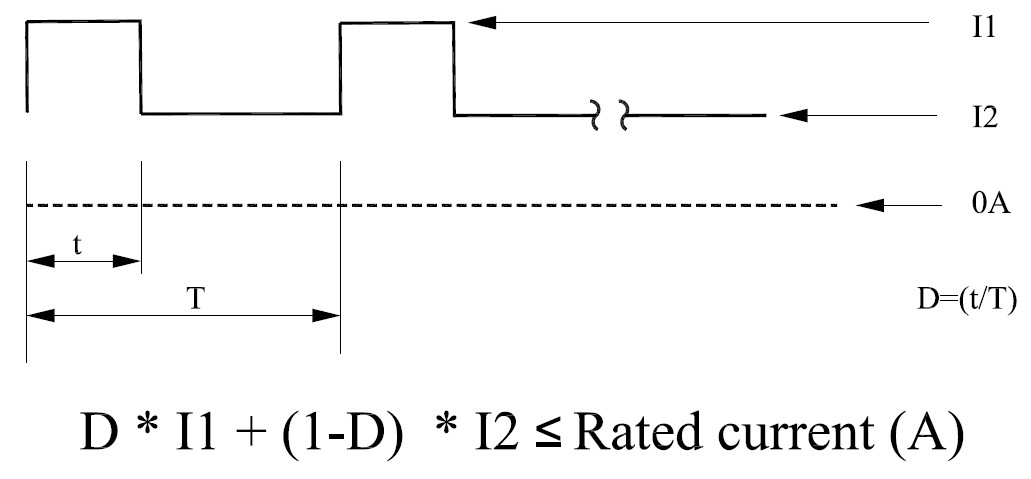
-
MTBF (Mean Time Between Failure)
Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) is a reliability term used to provide the amount of failure per million hours for a product.
-
Main Differences between IEC 60601-1 and IEC 60950-1
IEC 60601-1
IEC 60950-1
Leakage current
Earth leakage current: 0.5mA
Touch current: 0.1mA
Earth leakage current: 3.5mA
Touch current: 0.25mA
Dielectric strength test voltages (250V)
Input to Output: 4000Vac
Input to Ground: 1500Vac
Output to Ground: 1500Vac
Input to Output: 3000Vac
Input to Ground: 1500Vac
Output to Ground: 500Vac
Creepage distances / Air clearance (250V)
Basic Insulation: 4.0/2.5mm
Reinforced Insulation: 8.0/5.0mm
Basic Insulation: 2.5/2.0mm
Reinforced Insulation: 5.0/4.0mm
